Lesson structure used within the project.
Lesson structure used within the project
The basis of the digital pedagogy structure is established on the practical experiences that are complemented by the pedagogical theories about metacognition, reflection, and lesson structuring. The process supports teachers’ professional development through reflection; improvement of their teaching practices in an innovative manner and developing their own digital competencies.
Throughout the project, was used by the teachers as a systematic structure for implementing their own digital pedagogy.
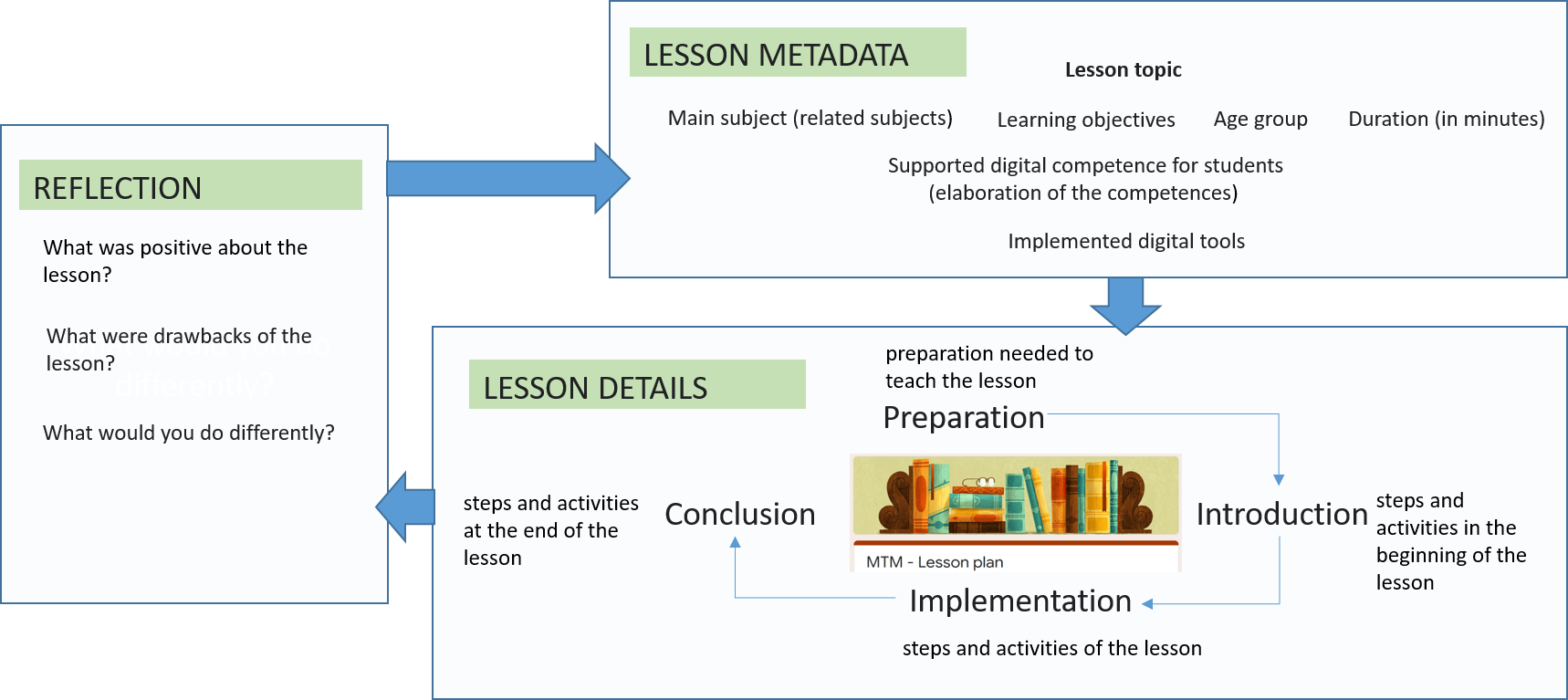
On the figure are presented three main phases which scaffold each other and act as guidelines. For the teacher, we have designed a structured form for designing a lesson. The form covers all the following phases.
- a) Lesson Metadata. During this phase, the teacher sets and describes key learning objectives and digital competencies that will be covered by the planned lesson. Learning objectives are derived from the curriculum and are topic-based. More complicated is with digital competence but it might be differently covered in the curricula of the countries. For example, since 2014 in Estonia digital competencies are embedded into the national curricula as one of the general competence. The solution here would be to rely on digital competencies based on the EU DIGCOMP framework. In our form, the guide the teacher to think on the following digital competencies: Information and data literacy, communication and collaboration, Digital content creation, Safety, Problem-solving.
- b) Lesson details: During this phase, the teacher describes activities that will be implemented during the lesson. Traditionally lesson is divided into four parts — preparation (preparing learning material, checking digital tools and connections), introduction (an overview of activities planned for the first part of the lesson), implementation (description of the learning activities and tasks), conclusion (description of concluding activities, e.g., gathering student feedback).
- c) Reflection: During this phase, the teacher analysis the lesson and the whole teaching process. The aim is to learn from the experience and apply this in a new similar situation. Here is helpful to use reflective questions, which help to set focus on certain aspects of the whole phases. This means that teachers can choose whether to reflect on Lesson Metadata or Lesson details phase or reflect on both. Common guiding questions for this are: what was positive about the lesson, what were the drawbacks of the lesson, or what would you do next time differently.